Human Uteroglobin / SCGB1A1 Protein (His Tag)
CC10,CC16,CCPBP,CCSP,UGB,UP-1,UP1
- 100ug (NPP4379) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10808-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CC10,CC16,CCPBP,CCSP,UGB,UP-1,UP1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SCGB1A1 consists of 81 amino acids and migrates as a 9.2 kDa band as predicted in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 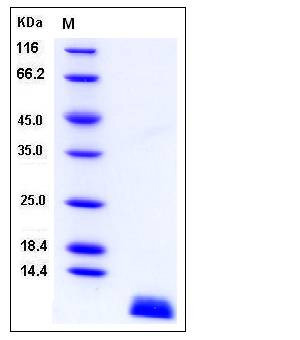 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SCGB1A1 (P11684) (Met 1-Asn 91) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of the A549 human lung carcinoma cell line. When 5 x 10E4cells/well are added to human SCGB1A1 coated plates (2 μg/ml and 100 μl/well), approximately >30% will adhere after one hour at 37 ℃. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Inflammatory Mediators |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Uteroglobin (UG), also known as Secretoglobin 1A member 1 (SCGB1A1), Blastokinin, Clara cell secretor protein (CCSP) or Clara cell-specific 10-kDa protein (CC10), is the founding member of the secretoglobin family of small, secreted, disulfide-bridged dimeric proteins found only in mammals. This protein is mainly expressed in lung, with anti-inflammatory/immunomodulatory properties. Previous in vitro studies demonstrated that CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBPs) are the major transcription factors for the regulation of SCGB1A1 gene expression, whereas FOXA1 had a minimum effect on the transcription. Uteroglobin is a multifunctional protein with antiinflammatory/immunomodulatory properties. Uteroglobin inhibits soluble phospholipase A(2) activity and binds and perhaps sequesters hydrophobic ligands such as progesterone, retinols, polychlorinated biphenyls, phospholipids, and prostaglandins. In addition to its antiinflammatory activities, Uteroglobin manifests antichemotactic, antiallergic, antitumorigenic, and embryonic growth-stimulatory activities. The tissue-specific expression of the Uteroglobin gene is regulated by several steroid hormones, although a nonsteroid hormone, prolactin, further augments its expression in the uterus. Based on its anti-inflammatory and antiallergic properties, Uteroglobin is a potential drug target. The mechanism of Uteroglobin action is likely to be even more complex as it also functions via a putative receptor-mediated pathway. |
| Reference |
