Human VCL / Vinculin Protein (His Tag)
CMD1W,CMH15,HEL114,MV,MVCL
- 100ug (NPP2578) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10019-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CMD1W,CMH15,HEL114,MV,MVCL |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human VCL consists of 1077 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 118 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rhVCL is approximately 115 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 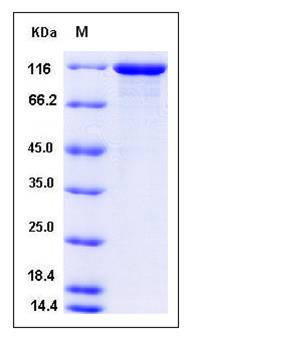 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human VCL (P18206-2) (Met 1-Gln 1066) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Akt Pathway |Phospholipases, Small GTPases, and Other Molecules in the Akt Pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Vinculin (VCL) is a cytoskeletal protein that is closely related to both cell-matrix interactions and cell-cell junctions. VCL is a membrane-cytoskeletal protein in focal adhesion plaques that is involved in linkage of integrin adhesion molecules to the actin cytoskeleton. The protein contains an acidic N-terminal domain and a basic C-terminal domain separated by a proline-rich middle segment. This protein has multi-ligand properties and has been found to interact with a number of microfilament associated proteins, such as talin, a-actinin, and paxillin, which reportedly bind to either the head or tail domains of vinculin. |
| Reference |
