Human VDR / NR1I1 Protein (His Tag)
NR1I1,PPP1R163
- 100ug (NPP4384) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12025-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | NR1I1,PPP1R163 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human VDR consists of 437 amino acids and migrates as an approximately 50 KDa band in SDS-PAGE in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 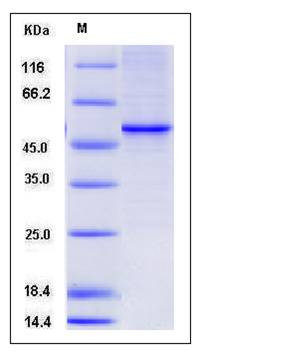 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human VDR (P11473) (Met 1-Ser 427) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Angiogenesis Growth Factor & Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% glycerol 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | VDR (vitamin D(1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3)receptor), also known as NR1I1, belongs to the NR1I family, NR1 subfamily. It is composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal ligand-binding domain. Vitamin D receptors (VDRs) are members of the NR1I family, which also includes pregnane X (PXR) and constitutive androstane (CAR) receptors, that form heterodimers with members of the retinoid X receptor family. VDRs repress expression of 1alpha-hydroxylase (the proximal activator of 1,25(OH)2D3) and induce expression of the 1,25(OH)2D3 inactivating enzyme CYP24. Also, it has recently been identified as an additional bile acid receptor alongside FXR and may function to protect gut against the toxic and carcinogenic effects of these endobiotics. VDR is expressed in the intestine, thyroid and kidney and has a vital role in calcium homeostasis. It is the nuclear hormone receptor, also called transcription factor that mediates the action of vitamin D3. Inherited mutations in the VDR gene leads to rickets. |
| Reference |
