Human VNN2 / Vanin-2 Protein (His Tag)
FOAP-4,GPI-80,VNN2
- 100ug (NPP4391) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11728-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | FOAP-4,GPI-80,VNN2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human VNN2 consists of 481 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 54.6 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhVNN2 is approximately 55-60 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 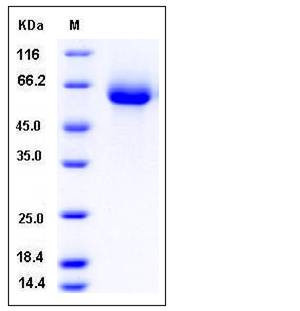 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human VNN2 isoform 1 (NP_004656.2) without the propeptide (Met 1-Ser 492) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Vascular non-inflammatory molecule 2, also known as glycosyl-phosphatidyl inositol-anchored protein GPI-80, Vanin-2, Protein FOAP-4 and VNN2, is a cell membrane protein which belongs to the CN hydrolase family and Vanin subfamily. VNN2 is widely expressed with higher expression in spleen and blood. VNN2 is a member of the vanin family of proteins which share extensive sequence similarity with each other, and also with biotinidase. The family includes secreted and membrane-associated proteins, a few of which have been reported to participate in hematopoietic cell trafficking. No biotinidase activity has been demonstrated for any of the vanin proteins, however, they possess pantetheinase activity, which may play a role in oxidative-stress response. VNN2 is an amidohydrolase that hydrolyzes specifically one of the carboamide linkages in D-pantetheine thus recycling pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) and releasing cysteamine. It is involved in the thymus homing of bone marrow cells. VNN2 plays a role in transendothelial migration of neutrophils and may regulate beta-2 integrin-mediated cell adhesion, migration and motility of neutrophil. |
| Reference |
