Human VSIG4 Protein (His Tag)
CRIg,Z39IG
- 100ug (NPP4394) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12163-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CRIg,Z39IG |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human VSIG4 consists of 275 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 30.5 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhVSIG4 is approximately 45 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Arg 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 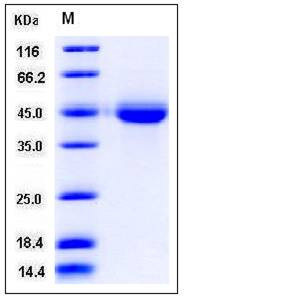 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human VSIG4 (Q9Y279-1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Pro 283) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Inflammatory Mediators |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | VSIG4 (V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4), also known as complement receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily (CRIg) and Z39Ig, is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein. It is a B7 family-related protein and an Ig superfamily member. In contrast to the B7 family members which contain two IgG domains, VSIG4 contains one complete V-type I g domain and a truncated C-type I g domain. VSIG4 is exclusively expressed on tissue resident macrophages and binds to multimers of C3b and iC3b that are covalently attached to particle surfaces. No VSIG4 expression appears to be present in T and B cells. VSIG4 functions as a negative regulator of T cell activation, and may be involved in the maintenance of peripheral T cell tolerance, and is also identified as a potent suppressor of established inflammation. Mouse VSIG4 is synthesized as a 280 amino acid precursor that contains a signal sequence, an V-type I g domain (aa 36-115), one potential N-linked glycosylation site, and a single transmembrane domain. The V-type I g domain of mouse VSIG4 shares 86% and 80% aa sequence identity with the V-type I g domains of rat and human VSIG4, respectively. |
| Reference |
