Human Vaspin / SerpinA12 Protein (His Tag)
OL-64
- 100ug (NPP4380) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11822-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | OL-64 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SERPINA12 consists of 405 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 46.5 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh SERPINA12 is approximately 50-55 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Leu 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 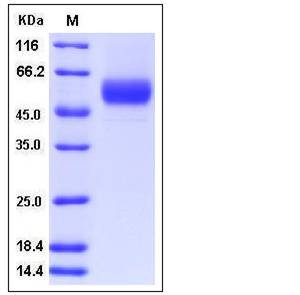 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SERPINA12 (NP_776249.1) (Met 1-Lys 414) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Plasma Cascade Systems in Inflammation |Fibrinolysis System |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Serpins are the largest and most diverse family of protease inhibitors. Most serpins control proteolytic cascades, certain serpins do not inhibit enzymes, but instead perform diverse functions such as storage (ovalbumin, in egg white), hormone carriage proteins (thyroxine-binding globulin, cortisol-binding globulin) and tumor suppressor genes (maspin). Most inhibitory serpins target chymotrypsin-like serine proteases. These enzymes are defined by the presence of a nucleophilic serine residue in their catalytic site. Some serpins inhibit other classes of protease. A number of such serpins have been shown to target cysteine proteases. These enzymes differ from serine proteases in that they are defined by the presence of a nucleophilic cysteine residue, rather than a serine residue, in their catalytic site. SerpinA12, also known as OL-64, Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor, Vaspin, Visceral adipose-specific serpin and SERPINA12, is a secreted protein which belongs to the serpin family. SerpinA12 / Vaspin is expressed in visceral adipose tissues. It may modulates insulin action conceivably only in the presence of its yet undefined target proteases in white adipose tissues. SerpinA12 / Vaspin may be the compensatory molecule in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome and SerpinA12 / Vaspin recombinant protein or vaspin-mimicking agents such as vaspin analogs, antibodies or small molecule agents may be the link to drug discovery and development. |
| Reference |
