Human WFIKKN2 / GASP-1 Protein (His Tag)
GASP-1,hGASP-1,WFDC20B,WFIKKNRP
- 100ug (NPP4397) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11998-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | GASP-1,hGASP-1,WFDC20B,WFIKKNRP |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human WFIKKN2 consists of 553 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 61.4 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhWFIKKN2 is approximately 70-75 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Leu 35 |
| SDS-PAGE | 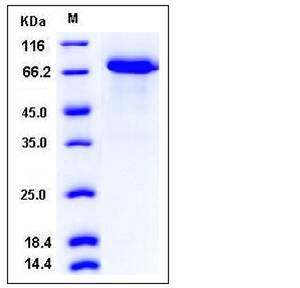 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human WFIKKN2 (NP_783165.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-His 576) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Adhesion molecule |Extracelluar matrix |Extracellualr matrix proteases & regulators |MMP regulators | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | WAP, kazal, immunoglobulin, kunitz and NTR domain-containing protein 2, also known as Growth and differentiation factor-associated serum protein 1, WAP, follistatin, immunoglobulin, kunitz and NTR domain-containing-related protein, WFIKKN-related protein, WFIKKN2 and GASP1, is a secreted protein which belongs to the WFIKKN family. WFIKKN2 contains two BPTI/Kunitz inhibitor domains, one Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain, one Kazal-like domain, one NTR domain and one WAP domain. WFIKKN2 is primarily expressed in ovary, testis and brain, but not in liver. In fetal tissues, it is primarily expressed in brain, skeletal muscle, thymus and kidney. WFIKKN2 is protease-inhibitor that contains multiple distinct protease inhibitor domains. It probably has serine protease- and metalloprotease-inhibitor activity. It inhibits the biological activity of mature myostatin, but not activin. WFIKKN2 protein binds mature GDF8/myostatin and myostatin propeptide and inhibits the biological activity of myostatin. |
| Reference |
