Human WTAP Protein (GST Tag)
Mum2
- 100ug (NPP2582) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12018-H09E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | Mum2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human WTAP/GST chimera consists of 386 amino acids and migrates as an approxiamtely 45 kDa band as predicted in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 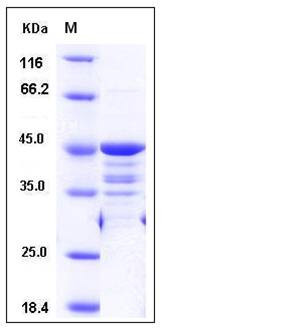 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human WTAP isoform 2 (Q15007-2) (Met 1-Arg 151) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Transcription |Other factors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 0.15M NaCl, 0.5mM GSH, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Wilms' tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) was previously identified as a protein associated with Wilms' tumor-1 (WT-1) protein that is essential for the development of the genitourinary system. WT1 was originally identified as a tumor suppressor for Wilms' tumor, but it is also overexpressed in a variety of cancer cells. The WTAP-WT1 axis in vascular cells suggest that WTAP is a vital and multifaceted regulator of vascular remodeling. WTAP has been suggested to function in alternative splicing, stabilization of mRNA, and cell growth. Knocking down endogenous WTAP increased Smooth muscle cells (SMCs) proliferation, because of increased DNA synthesis and G(1)/S phase transition, together with reduced apoptosis. These effects could be the result of WTAP suppressing the transcriptional activity of WT1 in SMCs. WTAP may thus also play a role in messenger RNA processing in mammalian cells, either dependent on or independent of its interaction with WT1. |
| Reference |
