Human c-MET / HGFR Protein (aa 956-1390, His & GST Tag)
AUTS9,c-Met,DFNB97,HGFR,RCCP2
- 100ug (NPP1099) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10692-H20B1 |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | AUTS9,c-Met,DFNB97,HGFR,RCCP2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human MET /GST chimera consists of 672 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 76.8 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 68 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 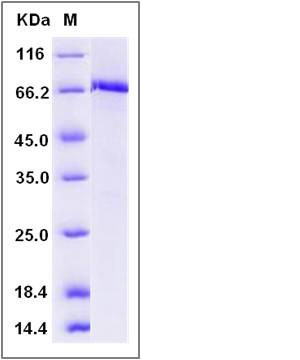 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human MET (P08581-1) (Lys956-Ser1390) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. The specific activity was determined to be 10 nmol/min/mg using MBP as substrate. 2. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human HGFR (aa 956-1390) (P 10692-H20B1) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human HGF-his (P 10463-H08H) with a linear range of 15.6-125 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Protein Phosphorylation |Tyrosine Kinase |Receptor Tyrosine Kinases |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% glycerol, 3mM DTT 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR), also known as c-Met or mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (MET), is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that has been shown to be overexpressed and/or mutated in a variety of malignancies. HGFR protein is produced as a single-chain precursor, and HGF is the only known ligand. Normal HGF/HGFR signaling is essential for embryonic development, tissue repair or wound healing, whereas aberrantly active HGFR has been strongly implicated in tumorigenesis, particularly in the development of invasive and metastatic phenotypes. HGFR protein is a multifaceted regulator of growth, motility, and invasion, and is normally expressed by cells of epithelial origin. Preclinical studies suggest that targeting aberrant HGFR signaling could be an attractive therapy in cancer. |
| Reference |
