Human cIAP1 / HIAP2 Protein (AVI Tag)
API1,c-IAP1,cIAP1,Hiap-2,HIAP2,MIHB,RNF48
- 100ug (NPP3741) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11090-H17E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | API1,c-IAP1,cIAP1,Hiap-2,HIAP2,MIHB,RNF48 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human cIAP1 consists of 230 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 26.5 kDa as estimated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly |
| SDS-PAGE | 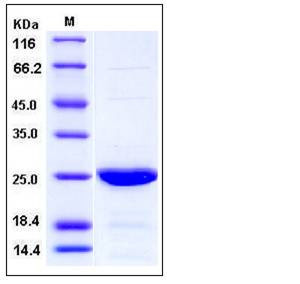 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the BIR2 & BIR3 domains (Glu 144-Leu 356) of human cIAP1 (NP_001157.1) was expressed, fused with the AVI tag at the C-terminus, and two additional amino acids (Gly & Pro) at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit DEVD-AFC cleavage activity in cell extracts activated by addition of cytochrome c and dATP. The IC50 for this effect is typically 450-750 nM . |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolism processes |Apoptosis |Caspase | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 10mM Tris, 5% glycerol, 0.5mM EDTA, 5mM DTT, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein-1 (cIAP1) is a member of the Inhibitor of Apoptosis family proteinsare (IAP) whose members are characterized by a novel domain of about 70 amino acids termed baculoviral IAP repeats (BIRs). The BIR domains of cIAP1 and cIAP2 bind to caspases, the key effector proteases of apoptosis. The IAP protein family which can enhance cell survival are crucial regulators of programmed cell death. Both cIAP1 and cIAP2 are the E3 ubiquitin protein isopeptide ligases for Smac, taking part in promoting cancer survival through functioning as E3 ubiqitin ligases. Removal of cIAP1 by genetic deletion may result in NF-κB signaling activation that induces TNFα production and in killing sensitive tumor cells through enhanced TNF-R1 death-receptor signaling and caspase 8 activation. The substrate-dependent E3 activity of cIAPs is mediated by their RING domains and is dependent on the specific interactions between cIAPs and Smac. cIAP1 and cIAP2 are also reported to be regulators of NF-kB activation upon TNFαtreatment. |
| Reference |
