Human nemo-like kinase / NLK Protein (His & GST Tag)
LAK1, NLK
- 100ug (NPP4118) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11573-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | LAK1, NLK |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human NLK /GST chimera consists of 644 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 74.1 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 73 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 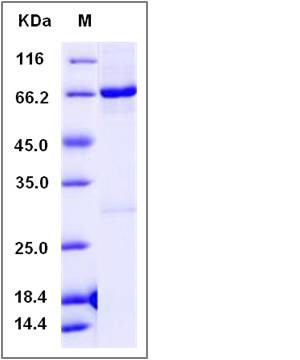 |
| Purity | > 91 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human NLK (Q9UBE8) (Val121-Glu527) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | The specific activity was determined to be 3 nmol/min/mg using MBP as substrate. |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Apoptosis |Nuclear |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Nemo-like kinase contains 1 protein kinase domain and belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family and MAP kinase subfamily. It also contains a TQE activation loop motif in which autophosphorylation of the threonine residue (Thr-298) is sufficient for kinase activation. As a serine/threonine-protein kinase, nemo-like kinase regulates a number of transcription factors with key roles in cell fate determination. It is a positive effector of the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway, acting downstream of WNT5A, MAP3K7/TAK1 and HIPK2. Activation of this pathway causes binding to and phosphorylation of the histone methyltransferase SETDB1. The NLK-SETDB1 complex subsequently interacts with PPARG, leading to methylation of PPARG target promoters at histone H3K9 and transcriptional silencing. The resulting loss of PPARG target gene transcription inhibits adipogenesis and promotes osteoblastogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Nemo-like kinase also is a negative regulator of the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. |
| Reference |
