MERS-CoV (NCoV / Novel coronavirus) Spike Protein S1 Protein (aa 1-725, His Tag)
S
- 100ug (NPP2966) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P40069-V08B1 |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | MERS-CoV |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | S |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant spike protein S1 (Human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012) comprises 719 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 79.9 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 94 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Tyr 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 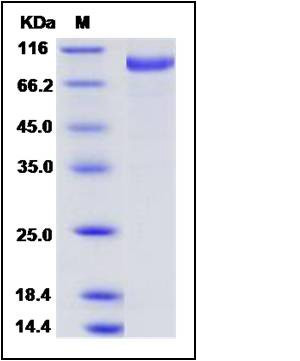 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the spike protein S1 (Human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012)(AFS88936.1)(Met1-Glu725) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Spike Protein S1 (aa 1-725) (P 40069-V08B1) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human DPP4 (P 10688-HNCH). The EC50 of of biotinylated DPP4 (P 10688-HNCH) is 0.52-1.22 μg/ml. 2. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Spike Protein S1 (aa 1-725) (P 40069-V08B1) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated Fc-DPP4 (P 10688-H01H). The EC50 of biotinylated Fc-DPP4 (P 10688-H01H) is 0.02-0.06 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Microbiology |Pathogenic microorganism |viruses |animal virus |Virus antigen |CoV viral antigen | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The spike (S) glycoprotein of coronaviruses contains protrusions that will only bind to certain receptors on the host cell: they are essential for both host specificity and viral infectivity. The term 'peplomer' is typically used to refer to a grouping of heterologous proteins on the virus surface that function together. The spike (S) glycoprotein of coronaviruses is known to be essential in the binding of the virus to the host cell at the advent of the infection process. Most notable is severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). The severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) spike (S) glycoprotein alone can mediate the membrane fusion required for virus entry and cell fusion. It is also a major immunogen and a target for entry inhibitors. The SARS-CoV spike (S) protein is composed of two subunits; the S1 subunit contains a receptor-binding domain that engages with the host cell receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and the S2 subunit mediates fusion between the viral and host cell membranes. The S protein plays key parts in the induction of neutralizing-antibody and T-cell responses, as well as protective immunity, during infection with SARS-CoV. |
| Reference |
