Mouse ACVR2A / ActrIIa Protein (His & Fc Tag)
ActrIIa,Acvr2,TactrII
- 100ug (NPP1040) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50613-M03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ActrIIa,Acvr2,TactrII |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse ACVR2A/Fc chimera is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 363 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 41.4 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 55-65 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ala 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 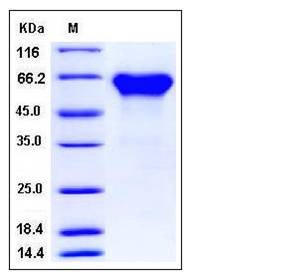 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse ACVR2A (NP_031422.3) (Met 1-Pro 134) was fused with the C-terminal polyhistidine-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to neutralize Activin-mediated inhibition on MPC11 cell proliferation. The ED50 for this effect is typically 20-60 ng/mL in the presence of 10 ng/mL recombinant Activin A. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Growth Factor & Receptor |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Superfamily |TGF-beta Superfamily Receptors | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ACVR2A and ACVR2B are two activin type II receptors. ACVR2A has been shown to interact with INHBA, SYNJ2BP and ACVR1B. The bovine ACVR2A gene encodes a protein of 513 amino acids which is highly homologous (approximately 98% identity) to the rat, mouse, and human ACVR2A proteins. Inactivation of ACVR2A is a common event in prostate cancer cells suggesting it may play an important role in the development of prostate cancer. The ACVR2A gene is a putative tumor suppressor gene that is frequently mutated in microsatellite-unstable colon cancers (MSI-H colon cancers). Frameshift mutation of ACVR2A may contribute to MSI-H colon tumorigenesis via disruption of alternate TGF-beta effector pathways. |
| Reference |
