Mouse ALCAM / CD166 Protein (His & Fc Tag)
AI853494,BEN,CD166,DM-GRASP,MuSC,SC1
- 100ug (NPP3213) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50005-M03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AI853494,BEN,CD166,DM-GRASP,MuSC,SC1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse ALCAM/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer after removal of the signal peptide. The reduced monomer consists of 748 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 84.2 kDa. Due to glycosylation, in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, rmALCAM/Fc migrates with approximately molecular mass of 105-110 kDa & 210 kDa corresponding to the monomer and homodimer. |
| predicted N | Trp 28 |
| SDS-PAGE | 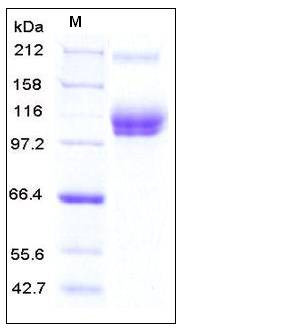 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Lys 527) of mouse ALCAM (NP_033785.1) precursor was fused with the C-terminal polyhistidine-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Immobilized mouse CD6-His (P50711-M08H) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind mouse ALCAM-Fc2h, The EC50 of mouse ALCAM-Fc2h is 0.12-0.28 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Embryogenesis |Germ Layer Formation |Mesoderm Marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM)/Cluster of differentiation (CD166) is a type I transmembrane cell adhesion molecule belonging to the Ig superfamily and a ligand for CD6 that is expressed on T lymphocytes. The extracellular domain of ALCAM contains five Ig-like domains (three Ig-like C2-type domains and two Ig-like V-type domains), of which the amino-terminal V1 domain is essential for ligand binding and ALCAM-mediated cell aggregation. ALCAM mediates both heterophilic (ALCAM-CD6) and homophilic (ALCAM-ALCAM) cell-cell interactions. ALCAM/CD6 interaction plays a role in T cell development and T cell regulation, as well as in the binding of T- and B-cells to activated leukocytes. Recently, homophilic (ALCAM-ALCAM) adhesion was shown to play important roles in tight cell-to-cell interaction and regulation of stem cell differentiation. While expressed in a wide variety of tissues, ALCAM is usually restricted to subsets of cells involved in dynamic growth and/or migration, including neural development, branching organ development, hematopoiesis, immune response and tumor progression. And CD166 is regarded as a potential novel breast cancer indicator and therapeutic target. |
| Reference |
