Mouse ASAM / CLMP Protein (His Tag)
9030425E11Rik,ACAM,ASP5,AW557819
- 100ug (NPP2660) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50553-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 9030425E11Rik,ACAM,ASP5,AW557819 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse ASAM consists of 226 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 25.6 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rm ASAM is approximately 33-36 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Thr 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 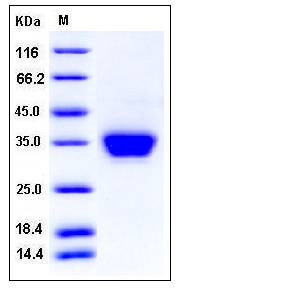 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse ASAM (Q8R373-1) (Met 1-Met 232) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of the HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cell line . When 4 x 10E4 cells/well are added to mouse ASAM coated plates (30 μg/ml, 100 μl/well), approximately >40 % will adhere after one hour at 37 ℃. |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurology process |Neurodegeneration and Neurodegenerative Disease |Others in Neurodegeneration and Neurodegenerative Disease |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Adipocyte-specific adhesion molecule (ASAM), also known as ACAM and CLMP, is a type I transmembrane protein and a member of the CTX (cortical thymocyte marker in Xenopus) family within the immunoglobulin superfamily. ASAM protein is highly expressed in the small intestine and placenta, and is found at intermediate levels in the heart, skeletal muscle, colon, spleen, kidney, and lung, and appears in low levels in the liver and peripheral blood leukocytes as well. ASAM is a transmembrane component of tight junctions in epithelial cells that can mediate cell aggregation and regulate transepithelial resistance across polarized epithelial cells. In addition, its expression is strongly correlated with white adipose tissue (WAT) mass of human and rodents with obesity. |
| Reference |
