Mouse Arylsulfatase A / ARSA Protein (His Tag)
As-2,AS-A,As2,ASA,AW212749,TISP73
- 100ug (NPP3177) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50018-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | As-2,AS-A,As2,ASA,AW212749,TISP73 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse ARSA consists of 500 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 53.5 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 60 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ser 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 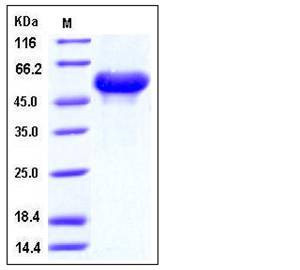 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Ser 506) of mouse ARSA (NP_033843.2) precursor was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave p-Nitrocatechol Sulfate (PNCS) . The specific activity is >100 pmoles/min/μg . |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Lysosomal Enzymes |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 25mM Tris, 0.15mM NaCl, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Arylsulfatase A (ARSA) is synthesized as a 52KDa lysosomal enzyme. It is a member of the sulfatase family that is required for the lysosomal degradation of cerebroside-3-sulfate, a sphingolipid sulfate ester and a major constituent of the myelin sheet. Arylsulfatase A is activated by a required co- or posttranslational modification with the oxidation of cysteine to formylglycine. Metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) is a lysosomal storage disease in the central and peripheral nervous systems with severe and progressive neurological symptoms caused by the deficiency of Arylsulfatase A. Deficiency of this enzyme is also found in apparently healthy individuals, a condition for which the term pseudodeficiency is introduced. ARSA forms dimers after receiving three N-linked oligosaccharides in the endoplasmic reticulum, and then the dimers are transported to the Golgi where they receive mannose 6-phosphate recognition markers. And thus, ARSA is transported and delivered to dense lysosomes in a mannose 6-phosphate receptor-dependent manner. It has been shown that within the lysosomes, the ARSA dimers can oligomerize to an octamer in a pH-dependent manner. The ARSA deficiency leads to metachromatic leucodystrophy (MLD), a lysosomal storage disorder associated with severe and progressive demyelination in he central and peripheral nervous system. Additionally, the serum level of arylsulfatase A might be helpful in diagnosis of lung and central nervous system cancer. |
| Reference |
