Mouse B7-DC / PD-L2 / CD273 Protein (His Tag)
B7-DC,Btdc,F730015O22Rik,PD-L2
- 100ug (NPP1075) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50804-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | B7-DC,Btdc,F730015O22Rik,PD-L2 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse PDCD1LG2 comprises 211 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 24 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rmPDCD1LG2 is approximately 35-45 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Leu 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 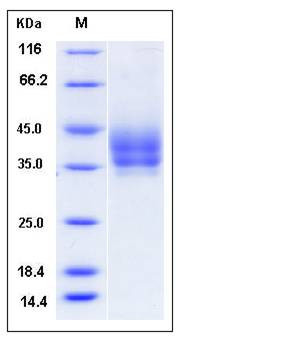 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse PDCD1LG2 (Q9WUL5) (Met 1-Arg 219) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized mouse PD-L2-his at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind mouse PD1-Fc. The EC50 of mouse PD1-Fc is 1.63 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Monocytes/Macrophages |Co-stimulatory Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Programmed death ligand 2 (PD-L2), also referred to as B7-DC and CD273, is a member of the B7 family of proteins including B7-1, B7-2, B7-H2, B7-H1 (PD-L1), and B7-H3. PD-L2 is a type I membrane protein and structurally consists of an extracellular region containing one V-like and one C-like Ig domain, a transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic domain. PD-L2 is expressed on antigen presenting cells, placental endothelium and medullary thymic epithelial cells, and can be induced by LPS in B cells, INF-γ in monocytes, or LPS plus IFN-γ in dendritic cells. The CD28 and B7 protein families are critical regulators of immune responses. PD-L2 and PD-L1 are two ligands for PD-1, member of the CD28/CTLA4 family expressed on activated lymphoid cells, and thus provide signals for regulating T cell activation and immune tolerance. The interaction of B7-DC/PD-1 exhibited a 2-6-fold higher affinity compared with the interaction of B7-H1/PD-1. |
| Reference |
