Mouse CAMK4 / CaMKIV Protein (His & GST Tag)
A430110E23Rik,AI666733,CaMKIV,CaMKIV/Gr,D18Bwg0362e
- 100ug (NPP2665) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50838-M20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | A430110E23Rik,AI666733,CaMKIV,CaMKIV/Gr,D18Bwg0362e |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse CAMK4/GST chimera consists of 706 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 80.4 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 85 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 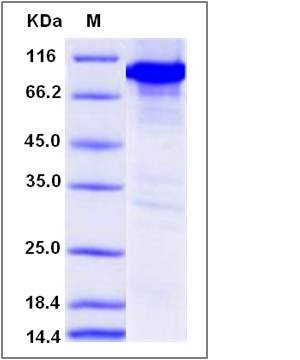 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse CAMK4 (P08414) (Met1-Tyr469) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | No Kinase Activity |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Kinase |Intracellular Kinase |Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase (CaM Kinase) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Ca2+/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 4 (CAMKⅣ) belongs to the serine/threonine protein kinase family, and to the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase subfamily which is widely recognized as an essential enzyme implicated in the phophoinositide amplification cascade. Ca2+/calmodulin dependent protein kinase (CAMK) can be activated by the introcellular increased Ca2+ and then apt to combine with the target protein. Ca2+/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 4 (CAMKⅣ) is a multifunctional CaM-dependent kinase protein with limited tissue distribution, that has been implicated in transcriptional regulation in lymphocytes, neurons and male germ cells. All of the isforms of this family, including myosin light chain kinase, phosphorylase kinase, CaMK1, CaMKⅢ and CaMKⅣ have EF-hand structure. |
| Reference |
