Mouse CD146 / MCAM Protein (His Tag)
1-gicerin,AV025631,CD146,CD149,Muc18,s-endo,s-gicerin
- 100ug (NPP3208) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50794-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 1-gicerin,AV025631,CD146,CD149,Muc18,s-endo,s-gicerin |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse MCAM comprises 551 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 61.3 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 90-100 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Val 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 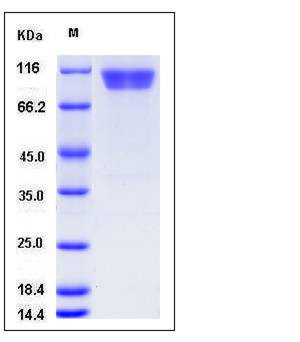 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse MCAM (Q8R2Y2-1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Val 563) was expressed, fused with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Embryogenesis |Germ Layer Formation |Mesoderm Marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The CD146 antigen, also known as melanoma cell adhesion molecule (MCAM) and MUC18, is an integral membrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD146 contains the characteristic immunoglobulin-like domains (V-V-C2-C2-C2), a transmembrane region and a short cytoplasmic tail. The CD146 expression is detected in endothelial cells in vascular tissue throughout the body, and plays a role in cell adhesion, as well as in cohesion of the endothelial monolayer at intercellular junctions in vascular tissue. As a Ca2+-independent cell adhesion molecule involved in heterophilic cell to cell interactions and a surface receptor, CD146 triggers tyrosine phosphorylation of FYN and PTK2 and subsequently induced signal transduction, proteolysis, or immune recognition. This protein is also expressed predominantly on metastatic lesions and advanced primary tumours, and thus has been suggested to play an important role in tumour progression and the development of metastasis in certain human carcinomas. |
| Reference |
