Mouse CD2 / LY37 Protein (His Tag)
LFA-2,Ly-37,Ly37
- 100ug (NPP3218) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50537-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | LFA-2,Ly-37,Ly37 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse CD2 consists of 192 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 22 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rmCD2 is approximately 35-45 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Arg 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 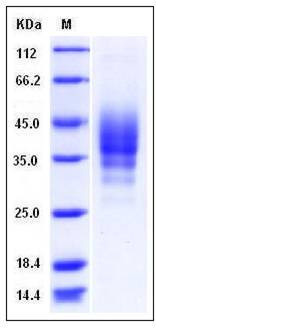 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse CD2 (NP_038514.1) (Met 1-Ser 203) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Adaptive Immunity |T Cell |T Cell CD Antigen |CD Antigen (T Cell Migration/Adhesion) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | T-cell surface antigen CD2, also known as T-cell surface antigen T11/Leu-5, and SRBC, is a single-pass type I membrane protein. It contains one Ig-like C2-type domain and one Ig-like V-type domain. CD2 is a cell adhesion molecule expressed on T cells and is recognized as a target for CD48 (rats) and CD58 (humans). CD2 has been shown to set quantitative thresholds in T cell activation both in vivo and in vitro. Further, intracellular CD2 signaling pathways and networks are being discovered by the identification of several cytosolic tail binding proteins. CD2 interacts with lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-3) and CD48/BCM1 to mediate adhesion between T-cells and other cell types. CD2 is implicated in the triggering of T-cells, the cytoplasmic domain of CD2 is implicated in the signaling function. The complex of CD2 and CD58 also plays an important role in enhancing the adhesion of T lymphocytes to target cells, and promoting hyperplasia and activation of T lymphocytes. As a cell surface glycoprotein, CD2 expressed on most human T cells and natural killer (NK) cells and plays an important role in mediating cell adhesion in both T-lymphocytes and in signal transduction. |
| Reference |
