Mouse CD27 / TNFRSF7 Protein (His Tag)
S152,Tnfrsf7,Tp55
- 100ug (NPP1132) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50110-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | S152,Tnfrsf7,Tp55 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse CD27 consists of 173 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and has a predicted molecular mass of 19.6 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, rmCD27 migrates as an approximately 35 kDa band due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Thr 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 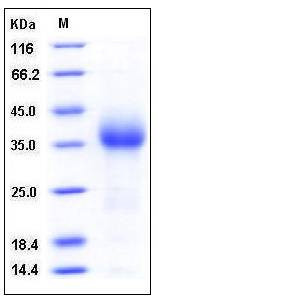 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Arg 182) of mouse CD27 (NP_001028298.1) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized recombinant mouse CD27 at 2 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human CD70 with a linear range of 78-1250 pg/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Regulation of Apoptosis by TNF Superfamily Members |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CD27, also known as TNFRSF7, is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily limited to cells of the lymphoid lineage, and exists as both a dimeric glycoprotein on the cell surface and as a soluble protein in serum. As a type I transmembrane glycoprotein of about 55 kDa existing as disulfide-linked homodimer, CD27 has been shown to play roles in lymphoid proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis.It has important role in generation of T cell immunity, and is an apparently robust marker for normal memory B cells. It is a T and B cell co-stimulatory molecule, the activity of CD27 is governed by its TNF-like ligand CD70 on lymphocytes and dendritic cells. The CD27-CD70 interaction is required for Th1 generation responses to differentiation signals and long-term maintenance of T cell immunity, and meanwhile, plays a key role in regulating B-cell differentiation, activation and immunoglobulin synthesis. |
| Reference |
