Mouse CD45 / PTPRC Protein (Fc Tag)
PTPRC
- 100ug (NPP3235) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50713-M02H1 |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | PTPRC |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse PTPRC /Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 643 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 71.7 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 118 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 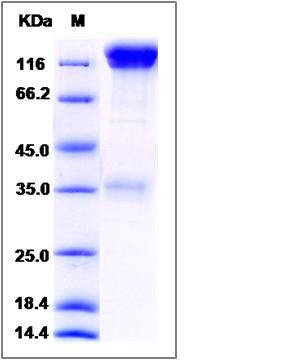 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse PTPRC (NP_035340.3) (Met1-Lys425) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human SEMA4D-His (P11825-H08H) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind mouse PTPRC-Fc with a linear range of 0.625-5 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Phosphatase & Regulator |Phosphatase Regulator |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The cluster of differentiation (CD) system is commonly used as cell markers in immunophynotyping. Different kinds of cells in the immune system can be identified through the surface CD molecules which associating with the immune function of the cell. There are more than 320 CD unique clusters and subclusters have been identified. Some of the CD molecules serve as receptors or ligands important to the cell through initiating a signal cascade which then alter the behavior of the cell. Some CD proteins do not take part in cell signal process but have other functions such as cell adhesion. Protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type C (CD45), also known as PTPRC is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family which is known for its function to serve as signaling molecules and to regulate a variety of cellular processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, mitotic cycle and oncogenic transformation. CD45 is found expression specifically in hemotopietic cells. CD45 consists of an extracellular domain, a single transmembrane segment and two tandem intracytoplasmic catalytic domains. It serves as an essential regulator of T-cell and B-cell antigen receptor signaling through either direct interaction with components of the antigen receptor complexs or by activating various Src family kinases required for the antigen receptor signaling and it also can suppress JAK kinases. |
| Reference |
