Mouse CD5L / CD5 antigen-like Protein (His Tag)
42010,AAC-11,AI047839,Api6,CT2,Pdp,Sp-alpha
- 100ug (NPP2685) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50020-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 42010,AAC-11,AI047839,Api6,CT2,Pdp,Sp-alpha |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse CD5L consists of 342 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 38 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rm CD5L is approximately 55-60 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 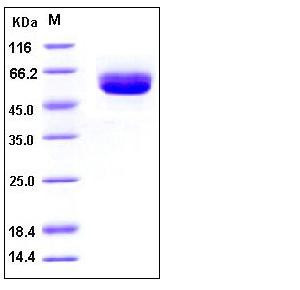 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Val 352) of mouse CD5L (NP_033820.2) precursor was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cluster of Differentiation (CD) |B Cell CD Antigen |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CD5L, also known as CD5 antigen-like, is a soluble protein belonging to group B of the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) superfamily and contains three SRCR domains. It is a secreted glycoprotein and expressed by macrophages presentin lymphoid tissues (spleen, lymph node, thymus, and bone marrow). It binds to myelomonocytic and lymphoid cells and may play an important role in the regulation of the innate and adaptive immune systems. CD5L functions as a pattern recognition molecule by binding both lipoteichoic acid (LTA) on Gram positive and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on Gram negative bacteria. and the SRCR domain 1 of CD5L retains both the LPS and LTA binding activities. In addtion, it is revealed that CD5L seems to play a role as an inhibitor of apoptosis. |
| Reference |
