Mouse CD64 / FCGR1 Protein (His Tag)
AI323638,AV092959,CD64,FcgammaRI,IGGHAFC
- 100ug (NPP3241) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50086-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AI323638,AV092959,CD64,FcgammaRI,IGGHAFC |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse FCGR1 consists of 284 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and has a predicted molecular mass of 32 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rm FCGR1 is approximately 45-50 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 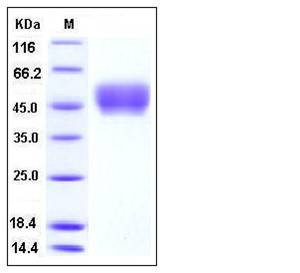 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Pro 297) of mouse FCGR1 (NP_034316.1) precursor was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized mouse CD64-His at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human IgG1, The EC50 of biotinylated human IgG1 is 0.07-0.17 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cluster of Differentiation (CD) |Monocyte/Macrophage CD Antigen |Macrophage Marker CD Antigen |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | High affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc receptor I, also known as FCGR1 and CD64, is an integral membrane glycoprotein and a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD64 is a high affinity receptor for the Fc region of IgG gamma and functions in both innate and adaptive immune responses. Receptors that recognize the Fc portion of IgG function in the regulation of immune response and are divided into three classes designated CD64, CD32, and CD16. CD64 is structurally composed of a signal peptide that allows its transport to the surface of a cell, three extracellular immunoglobulin domains of the C2-type that it uses to bind antibody, a hydrophobic transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic tail. CD64 is constitutively found on only macrophages and monocytes, but treatment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes with cytokines like IFNγ and G-CSF can induce CD64 expression on these cells. The inactivation of the mouse CD64 resulted in a wide range of defects in antibody Fc-dependent functions. Mouse CD64 is an early participant in Fc-dependent cell activation and in the development of immune responses. |
| Reference |
