Mouse CD69 / CLEC2C / AIM Protein (Fc Tag, ECD)
5830438K24Rik,AI452015,AIM,VEA
- 100ug (NPP3408) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50731-M01H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 5830438K24Rik,AI452015,AIM,VEA |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse Cd69 consists 396 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 44.1 kDa. |
| predicted N | Glu |
| SDS-PAGE | 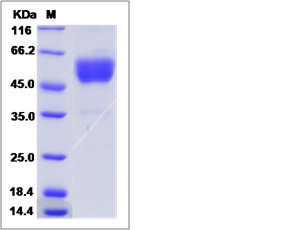 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse Cd69 (NP_001028294.1) (Gly64-Arg199) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cluster of Differentiation (CD) |T Cell CD Antigen |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Early activation antigen CD69, also known as activation inducer molecule (AIM), is a single-pass type II membrane protein. Recently, cDNA clones encoding human and mouse CD69 were isolated and showed CD69 to be a member of the C-type lectin superfamily. It is one of the earliest cell surface antigens expressed by T cells following activation. Once expressed, CD69 acts as a costimulatory molecule for T cell activation and proliferation. In addition to mature T cells, CD69 is inducibly expressed by immature thymocytes, B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, monocytes, neutrophils and eosinophils, and is constitutively expressed by mature thymocytes and platelets. CD69 is involved in lymphocyte proliferation and functions as a signal transmitting receptor in lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, and platelets. The structure, chromosomal localization, expression and function of CD69 suggest that it is likely a pleiotropic immune regulator , potentially important in the activation and differentiation of a wide variety of hematopoietic cells. This membrane molecule transiently expresses on activated lymphocytes, and its selective expression in inflammatory infiltrates suggests that it plays a role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. CD69 plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of allergen-induced eosinophilic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness and that CD69 could be a possible therapeutic target for asthmatic patients. |
| Reference |
