Mouse CD84 Protein (His Tag)
A130013D22Rik,CDw84,SLAMF5
- 100ug (NPP3247) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50757-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | A130013D22Rik,CDw84,SLAMF5 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse CD84 consists of 211 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 24 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rmCD84 is approximately 37-42 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Lys 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 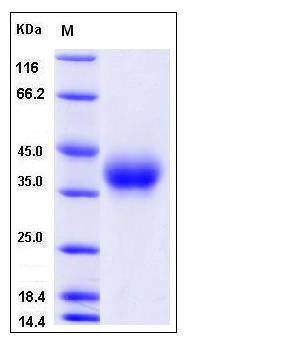 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse CD84 isoform 1 (Q18PI6-1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Val 221) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to bind biotinylated recombinant human SH2D1A in a functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The CD2 family receptors are type I transmembrane glycoproteins belonging to immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily characterized by a membrane-proximal Ig constant 2 (C2) domain and a membrane-distal variable (V) domain that is responsible for ligand recognition. CD84, also known as LY9B and SLAMF5, is a homophilic member of the SLAM (signaling lymphocyte activation molecule) subfamily of the CD2 family. The SLAM family receptorsmediate signal transduction through the interaction of its ITSM (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motifs) in the intracellular region and the SH2 domain of adaptor molecules SAP (SLAM-associated protein) and EAT-2 (EWS-activated transcript 2), and accordingly modulate both adaptive and innate immune responses. The CD84-CD84 interaction was independent of its cytoplasmic tail. Thus, CD84 is its own ligand and acts as a costimulatory molecule. CD84 is expressed on cells from almost all hematopoietic lineages and on CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells, suggesting that CD84 serves as a marker for committed hematopoietic progenitor cells. |
| Reference |
