Mouse CD99L2 / MIC2L1 Protein (Fc Tag)
AW548191,Mic2l1,Xap89
- 100ug (NPP3253) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50526-M02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AW548191,Mic2l1,Xap89 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse CD99L2/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer comprises 380 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 42 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rmCD99L2/Fc monomer is approximately 55-65 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Asp 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 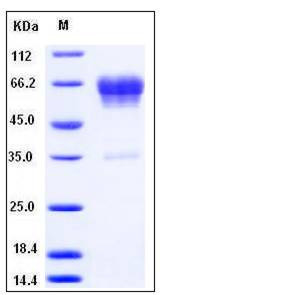 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse CD99L2 (NP_612182.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Ala 164) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Mouse CD99 antigen-like protein 2, also known as MIC2-like protein 1, CD99L2 and MIC2L1, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the CD99 family. CD99L2 is expressed in brain, heart, lung, liver, spleen, kidney, stomach, small intestine, skeletal muscle, ovary, thymus, testis and uterus. Lower expression of CD99L2 is seen in thymus. It is also expressed in E18 uterus and placenta. CD99 and CD99L2 were required for leukocyte extravasation in the cremaster after stimulation with tumor necrosis factor-alpha, where the need for PECAM-1 is known to be bypassed. CD99 and CD99L2 act independently of PECAM-1 in leukocyte extravasation and cooperate in an independent way to help neutrophils overcome the endothelial basement membrane. CD99L2 may function as a homophilic adhesion molecule. It functions in leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions during leukocyte extravasation, and in particular, at the diapedesis step. CD99L2 does not seem to be involved in docking of leukocytes to the vessel wall or in lymphocyte diapedesis. |
| Reference |
