Mouse CDCP1 Protein (Fc Tag)
9030022E12Rik,AA409659,E030027H19Rik
- 100ug (NPP3256) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P51110-M02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 9030022E12Rik,AA409659,E030027H19Rik |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse CDCP1 /Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 878 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 98.8 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 117 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ser 30 |
| SDS-PAGE | 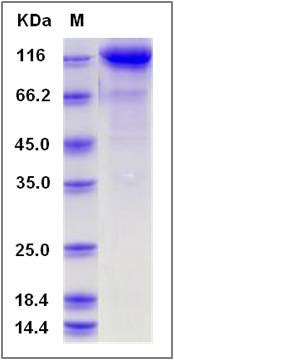 |
| Purity | > 79 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse CDCP1 (Q5U462) (Met1-Leu666) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Cell Adhesion Proteins |Cytoskeletal Proteins |Microfilaments |Actin etc |Actin Assembly | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CDCP1 contains three extracellular CUB domains. It is a putative stem cell marker that is highly expressed in some human cancer cells and in both, typical and atypical (cancerous) colons. It interacts with CDH2/N-cadherin, CDH3/P-cadherin, SDC1/syndecan-1, SDC4/syndecan-4 and the serine protease ST14/MT-SP1. It also interacts with SRC and PRKCG/protein kinase C gamma. CDCP1 is taken as a key regulator of EGF/EGFR-induced cell migration. It has been shown that signaling via EGF/EGFR induces migration of ovarian cancer Caov3 and OVCA420 cells with concomitant up-regulation of CDCP1 mRNA and protein. Consistent with a role in cell migration CDCP1 relocates from cell-cell junctions to punctate structures on filopodia after activation of EGFR. It may be involved in cell adhesion and cell matrix association. It also may play a role in the regulation of anchorage versus migration or proliferation versus differentiation via its phosphorylation. It has been taken as a novel marker for leukemia diagnosis and for immature hematopoietic stem cell subsets. |
| Reference |
