Mouse CES5 / Carboxylesterase-5 Protein (His Tag)
1700081L16Rik,1700122C07Rik,BB081581,cauxin,Ces7,Gm503
- 100ug (NPP2691) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50620-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 1700081L16Rik,1700122C07Rik,BB081581,cauxin,Ces7,Gm503 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse CES5 comprises 541 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 60.6 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 52 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 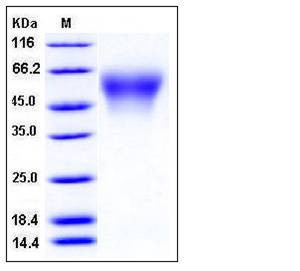 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse CES5 (NP_766347.1) (Met 1-His 556) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to hydrolyze pnitrophenylacetate. The specific activity is >50,000 pmoles/min/μg . |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Cancer |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 25mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Carboxylesterase belongs to the class of serine hydrolases family which includes Chymotrypsin and Acetylcholinesterase. Carboxylesterase is involved in the chemical reaction, exerting its role in catalyzing the carboxylic ester and water to convert to an alcohol and a carboxylate. Carboxylesterase is a type of enzyme that capable of hydrolyzing a variety of carboxylic acid esters and it's widely distributed in cells especially in mammalian liver. Carboxylesterase 5 (CES5), also known as cauxin or CES7, is one of CES enzyme families exerting role in catalyzing hydrolytic and transesterfication reactions with broad substrat specifity. CES5 is reported in high concentrations in the urine of adult male cats, and within a protein complex of mammalian male epididymal fluids. Roles for carboxylesterase 5 may include regulating urinary levels of cat pheromone, catalyzing lipid transfer reactions within mammalian male reproductive fluids, and protecting neural tissue from drugs and xenobiotics. |
| Reference |
