Mouse CHI3L1 / YKL40 / gp39 Protein (His Tag)
AW208766,Brp39,Gp39
- 100ug (NPP3259) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50929-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AW208766,Brp39,Gp39 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse CHI3L1 comprises 371 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 42.3 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rmCHI3L1 is approximately 50 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Tyr 371 |
| SDS-PAGE | 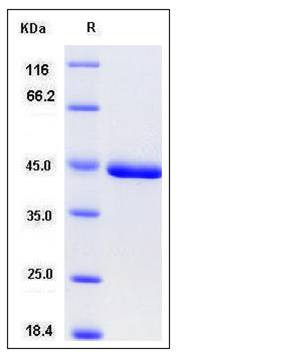 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse CHI3L1 (Q61362) (Met 1-Ala 381) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Lysosomal Enzymes |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Chitinase-3-like protein 1 (CHI3L1) is a secreted heparin-binding glycoprotein whose expression is associated with vascular smooth muscle cell migration. CHI3L1 is expressed at high levels in postconfluent nodular VSMC cultures and at low levels in subconfluent proliferating cultures. CHI3L1 is a tissue-restricted, chitin-binding lectin and member of glycosyl hydrolase family 18. In contrast to many other monocyto / macrophage markers, its expression is absent in monocytes and strong induced during late stages of human macrophage differentiation. Elevated levels of CHI3L1 are associated with disorders exhibiting increased connective tissue turnover, such as rheum atoid, arthritis, osteoarthritis, scleroderma, and cirrhosis of liver, but is produced in cartilage from old donors or patiens with osteoarthritis. CHI3L1 is abnormally expressed in the hippocampus of subjects with schizophrenia and may be involved in the cellular response to various environmental events that are reported to increase the risk of schizophrenia. |
| Reference |
