Mouse CHK1 / CHEK1 Protein (His & GST Tag)
C85740,Chk1,rad27
- 100ug (NPP3260) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50248-M20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | C85740,Chk1,rad27 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse CHEK1/GST chimera consists of 713 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 82.2 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 78 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 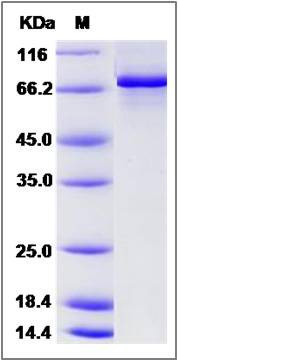 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse CHEK1 (O35280-1) (Met1-Thr476) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Kinase activity untested |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Checkpoint |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 8.5, 3mM DTT, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CHK1 / CHEK1 contains 1 protein kinase domain and belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family, NIM1 subfamily. It is a member of checkpoint kinases (Chks). Chks Checkpoint kinases (Chks) are serine/threonine kinases that are involved in the control of the cell cycle. There are two subtypes of chks that have so far been identified, CHK1 / CHEK1 and Chk2. They are essential components to delay cell cycle progression in normal and damaged cells and can act at all three cell cycle checkpoints. Chks are activated by phosphorylation. ATR kinase phosphorylates CHK1 / CHEK1 in response to single strand DNA breaks and ATM kinase phosphorylates Chk2 in response to double strand breaks. Chks phosphorylate Cdc25 phosphatase at Ser216, which leads to Cdc25 sequestration in the cytoplasm. Chks have a role in the physiological stress of hypoxia/reoxygenation. CHK1 / CHEK1 is required for checkpoint mediated cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage or the presence of unreplicated DNA. CHK1 / CHEK1 may also negatively regulate cell cycle progression during unperturbed cell cycles. |
| Reference |
