Mouse CNDP2 / CN2 / CPGL Protein (His Tag)
0610010E05Rik,C76600,Cn2,Dip-2,Pep-1,Pep1
- 100ug (NPP2702) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50246-M08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | 0610010E05Rik,C76600,Cn2,Dip-2,Pep-1,Pep1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse CNDP2 consists of 485 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 54 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 50 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 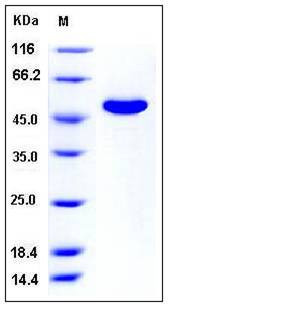 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse CNDP2 (NP_075638.2) (Met 1-Asn 475) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave carnosine (β-Ala-His) in a two step assay (mouse CNDP2 concentration 10 μg/ml). The specific activity is >40 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Cell cycle |Markers |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 0.5mM PMSF, 10% glycerol, pH 8.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Mouse cytosolic non-specific dipeptidase, also known as CNDP dipeptidase 2, Glutamate carboxypeptidase-like protein 1, Peptidase A, CNDP2 and CN2, is a cytoplasm protein which belongs to the peptidase M20A family. CNDP2 / CPGL is a cytosolic enzyme that can hydrolyze carnosine to yield l-histidine and beta-alanine. CNDP2 / CPGL hydrolyzes a variety of dipeptides including L-carnosine but has a strong preference for Cys-Gly. It may be play a role as tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. Isoform 1 of CNDP2 / CPGL is ubiquitously expressed with higher levels in kidney and liver (at protein level). Isoform 2 of CNDP2 / CPGL is expressed in fetal tissues, it is only expressed in adult liver and placental tissues. CNDP2 / CPGL is highly expressed in the histaminergic neurons in the tuberomammillary nucleus, implying that it may supply histidine to histaminergic neurons for histamine synthesis. |
| Reference |
