Mouse CTLA4 / CD152 Protein (His Tag)
Cd152,Ctla-4,Ly-56
- 100ug (NPP1212) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50503-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Cd152,Ctla-4,Ly-56 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse CTLA4 consists of 138 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 15.3 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rm CTLA4 is approximately 25-30 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 36 |
| SDS-PAGE | 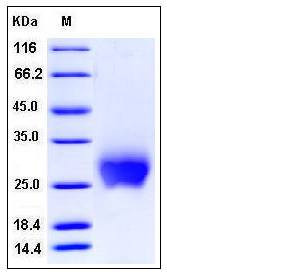 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse CTLA4 (NP_033973.2) (Met 1-Phe 162) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized recombinant mouse CTLA4-His (P50503-M08H) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can mouse CD80-Fc (cat:50446-M02H) with a linear range of 0.78-62.5 ng/ml. 3. Immobilized recombinant mouse CTLA4-His (P50503-M08H) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can human B7-1-Fc (P10698-H03H) with a linear range of 0.78-125 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Adaptive Immunity |Costimulation & Costimulatory Molecule |B7/CD28 Family |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4, also known as CTLA4 and CD152, is a single-pass type I membrane protein and a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is the second member of the CD28 receptor family. The ligands or counterreceptors for these two proteins are the B7 family members, CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2). CTLA4 transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells, whereas CD28 transmits a stimulatory signal. Intracellular CTLA4 is also found in regulatory T cells and may play an important role in their functions. CD152 or cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) is an essential receptor involved in the negative regulation of T cell activation. Because of its profound inhibitory role, CD152 has been considered a sound susceptible candidate in autoimmunity and a persuasive target for cancer immunotherapy. In particular, recent evidence suggests that CD152 is also important in the homeostasis and function of a population of suppressive cells, termed regulatory T cells (Treg). |
| Reference |
