Mouse CXADR Protein (His & Fc Tag)
2610206D03Rik,AU016810,AW553441,CAR,MCAR,MCVADR
- 100ug (NPP2709) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50019-M03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 2610206D03Rik,AU016810,AW553441,CAR,MCAR,MCVADR |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse CXADR/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer consists of 466 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 52 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rm CXADR/Fc monomer migrates with an apparent molecular mass of 60-65 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Leu 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 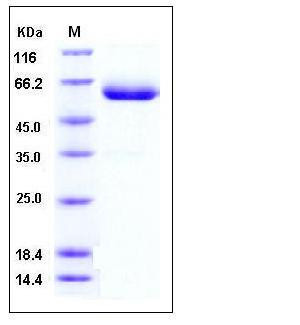 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse CXADR (NP_001020363.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Gly 237) was fused with the C-terminal polyhistidine-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of mouse neutrophils. When 5 x 10E4 cells/well are added to CXADR-coated plates (4 μg/ml and 100 μl/well), approximately 20%-40% will adhere specifically after 60 minutes at 37℃. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Tight Junctions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CXADR (coxsackie virus and adenovirus receptor), also known as CAR, is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the CTX family of the Ig superfamily, and is essential for normal cardiac development in the mouse. Proposed as a homophilic cell adhesion molecule, CXADR is a component of the epithelial apical junction complex that is essential for the tight junction integrity, and probably involved in transepithelial migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN). Mature mouse CXADR structrually comprises a 218 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with a V-type (D1) and a C2-type (D2) Ig-like domain, a 21 aa transmembrane segment and a 107 aa intracellular domain, among which,D1 is thought to be responsible for homodimer formation in trans within tight junctions. The ECD of mouse CXADR shares 97%, 90% sequence identity with the corresponding regions of rat, human CXADR. |
| Reference |
