Mouse Cathepsin E / CTSE Protein (His Tag)
A430072O03Rik,C920004C08Rik,CatE,CE
- 100ug (NPP2674) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50564-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | A430072O03Rik,C920004C08Rik,CatE,CE |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse CTSE (pro form) consists of 390 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 42.4 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rmCTSE is approximately 45-48 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 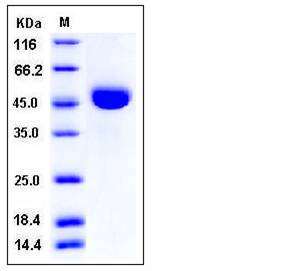 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse CTSE (NP_031825.2) (Met 1-Pro 397) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Lysosomal Enzymes |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cathepsin E Protein (CTSE Protein) is a member of the peptidase C1 family that is a gastric aspartic protease that functions as a disulfide-linked homodimer. Cathepsin E Protein (CTSE Protein) is predominantly present in the cells of immune system and is frequently implicated in antigen processing via the MHC classⅡ pathway which however does not appear to be involved in the digestion of dietary protein. The protein has a specificity similar to that of pepsin and pepsin. Cathepsin E Protein (CTSE Protein) is found in highest concentration in the surface of epithelial mucus-producing cells of the stomach and also been found in more than half of the gastric cancers. It appears, therefore, to be an oncofetal antigen. |
| Reference |
