Mouse Coagulation Factor II / FII / F2 Protein (His Tag)
Cf-2,Cf2,FII
- 100ug (NPP3270) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50344-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Cf-2,Cf2,FII |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse F2 consists of 605 amino acids (pro form) and has a calculated molecular mass of 69.3 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the recombinant mouse F2 is approximately 85 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 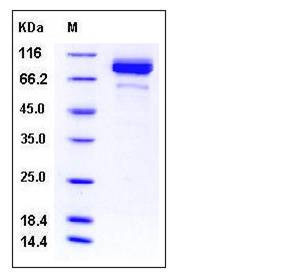 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the full length of mouse F2 (NP_034298.1) (Met 1-Gly 618) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate Boc-VPR-AMC R&D Systems, Catalog # ES011. The specific activity is > 2000 pmoles/min/μg. (Activation description: The proenzyme needs to be activated by Thermolysin for an activated form) |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Metabolic disorders |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Coagulation Factor II Protein (FII, F2 Protein or Prothrombin) is proteolytically cleaved to form thrombin in the first step of the coagulation cascade which ultimately results in the stemming of blood loss. Coagulation Factor II Protein (FII, F2 Protein) also plays a role in maintaining vascular integrity during development and postnatal life. Prothrombin / Coagulation Factor II is activated on the surface of a phospholipid membrane that binds the amino end of prothrombin / Coagulation Factor II and factor Va and Xa in Ca-dependent interactions; factor Xa removes the activation peptide and cleaves the remaining part into light and heavy chains. The activation process starts slowly because factor V itself has to be activated by the initial, small amounts of thrombin. Prothrombin / Coagulation Factor II is expressed by the liver and secreted in plasma. Defects in prothrombin / Coagulation Factor II are the cause of factor II deficiency (FA2D). It is very rare blood coagulation disorder characterized by mucocutaneous bleeding symptoms. The severity of the bleeding manifestations correlates with blood factor II levels. Defects in Coagulation Factor II are also a cause of susceptibility to thrombosis. It is a multifactorial disorder of hemostasis characterized by abnormal platelet aggregation in response to various agents and recurrent thrombi formation. |
| Reference |
