Mouse Coagulation Factor VII / FVII / F7 Protein (His Tag)
AI132620,Cf7,FVII
- 100ug (NPP3332) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50034-M08S |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | CHO Stable Cells |
| Synonyms | AI132620,Cf7,FVII |
| Molecular Weight | The mature form of mouse FⅦ consists of 416 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and the propeptid, and has a predicted molecular mass of 47 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rm FⅦ is approximately 56-63 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Val 25 & Ala 42 |
| SDS-PAGE | 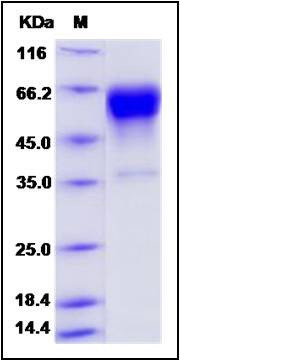 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse FⅦ (NP_034302.2) (Met 1-Leu 446) was fused with the a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized mouse F7-his at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated mouse F3-his (Cat:50413-M08H). The EC50 of biotinylated mouse F3-his (Cat:50413-M08H) is 0.1-0.3 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Plasma Cascade Systems in Inflammation |Complement System |Regulatory |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Coagulation factor VII, also known as Serum prothrombin conversion accelerator, Factor VII, F7 and FVII, is a member of the peptidase S1 family. Factor VII is one of the central proteins in the coagulation cascade. It is an enzyme of the serine protease class, and Factor VII (FVII) deficiency is the most frequent among rare congenital bleeding disorders. Factor VII contains two EGF-like domains, one Gla (gamma-carboxy-glutamate) domain and one peptidase S1 domain. The main role of factor VII is to initiate the process of coagulation in conjunction with tissue factor (TF). Tissue factor is found on the outside of blood vessels, normally not exposed to the blood stream. The action of the Factor VII is impeded by tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), which is released almost immediately after initiation of coagulation. Factor VII is vitamin K dependent and is produced in the liver. Upon vessel injury, tissue factor is exposed to the blood and circulating Factor VII. Once bound to TF, FVII is activated to FVIIa by different proteases, among which are thrombin (factor IIa), factor Xa, IXa, XIIa, and the FVIIa-TF complex itself. Recombinant activated factor VII (rFVIIa) is a haemostatic agent, which was originally developed for the treatment of haemophilia patients with inhibitors against factor FVIII or FIX. FVIIa binds specifically to endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR), a known cellular receptor for protein C and activated protein C, on the endothelium. rFVIIa is a novel hemostatic agent, originally developed for the treatment of hemorrhage in hemophiliacs with inhibitors, which has been successfully used recently in an increasing number of nonhemophilic bleeding conditions. |
| Reference |
