Mouse Contactin 5 / CNTN5 Protein (His Tag)
CNTN5
- 100ug (NPP3268) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P51092-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CNTN5 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse CNTN5 comprises 1046 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 115.2 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 118 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Leu 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 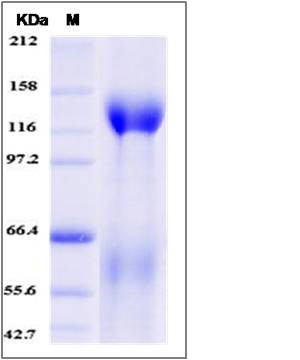 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse CNTN5 (P68500) (Met1-Gln1058) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of C6 cells. When 5 x 10E4 cells/well are added to CNTN5 coated plates (0.8 μg/mL and 100 μL/well), approximately >70% cells will adhere specifically after 60 minutes at 37℃. |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Sensory System |Auditory system |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Contactins are a subgroup of molecules belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily that are expressed mainly in the nervous system. The subgroup consists of six members: Contactin-1, Contactin-2(TAG-1), Contactin-3(BIG-1), BIG-2, Contactin-5(NB-2) and NB-3. Since their identification in the late 1980s, Contactin-1 and Contactin-2 have been studied extensively. Axonal expression and the neurite extension activity of Contactin-1 and Contactin-2 attracted researchers to study the function of these molecules in axon guidance during development. Contactin-1 and Contactin-2 have come to be known as the principal molecules in the function and maintenance of myelinated neurons. In contrast, the function of the other four members of this subgroup remained unknown until recently. Contactin-5, also known as NB-2, is one of the neural recognition molecules in the contactin subgroup. Contactin-5 is expressed in brain and kidney and at very low level in placenta. In brain, Contactin-5 is highly expressed in the occipital lobe, amygdala, cerebral cortex, frontal lobe, thalamus and temporal lobe. Mice deficient in the Contactin-5 gene exhibit aberrant responses to acoustic stimuli. Contactin-5 may play a role in maturation of glutamatergic synapses in the brainstem during the final stages of auditory development. Contactin-5 gene may contribute to human neurological disorders. |
| Reference |
