Mouse DDR2 Kinase / CD167b Protein (His Tag)
AW495251,Ntrkr3,tyro10
- 100ug (NPP3290) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50541-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AW495251,Ntrkr3,tyro10 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse DDR2 consists of 389 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 44 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rm DDR2 is approximately 80-90 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Lys 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 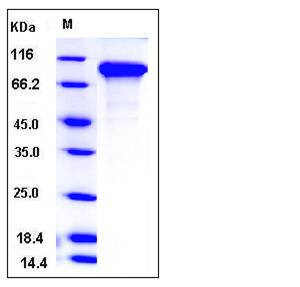 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse DDR2 (NP_072075.2) (Met 1-Arg 399) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to bind rat tail Collagen I in a functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) or CD167b (cluster of differentiation 167b) is a kind of protein tyrosine kinases associated with cell proliferation and tumor metastasis, and collagen, identified as a ligand for DDR2, up-regulates matrix metallloproteinase 1 (MMP-1) and MMP-2 expression in cellular matrix. DDR2/CD167b was found to recognise the triple-helical region of collagen X as well as the NC1 domain. Binding to the collagenous region was dependent on the triple-helical conformation. DDR2/CD167b autophosphorylation was induced by the collagen X triple-helical region but not the NC1 domain, indicating that the triple-helical region of collagen X contains a specific DDR2 binding site that is capable of receptor activation. DDR2/CD167b is induced during stellate cell activation and implicate the phosphorylated receptor as a mediator of MMP-2 release and growth stimulation in response to type I collagen. Moreover, type I collagen-dependent upregulation of DDR2/CD167b expression establishes a positive feedback loop in activated stellate cells, leading to further proliferation and enhanced invasive activity. |
| Reference | et al. |
