Mouse E-Cadherin / CDH1 / E-cad / CD324 Protein (His Tag)
AA960649, Ecad, L-CAM, MGC107495, UVO, Um
- 100ug (NPP3294) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50671-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AA960649, Ecad, L-CAM, MGC107495, UVO, Um |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse CDH1 (pro form) comprises 697 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 78 kDa. As a result of different glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rm CDH1 is approximately 80-100 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 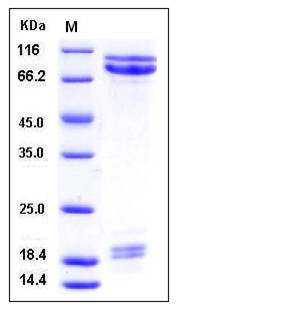 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse CDH1 (P09803) (Met 1-Val 709) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma cells. When 5 x 10E4 cells/well are added to Recombinant Mouse Cadherin-1 coated plates (0.8 μg/mL with 100 μL/well), approximately >50% will adhere after 1 hour at 37℃. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Adhesion molecule |Cell adhesion |Cadherins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cadherins are calcium-dependent cell adhesion proteins which preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells, and thus may contribute to the sorting of heterogeneous cell type. E-cadherin (E-Cad), also known as CDH1 and CD324, is a calcium-dependent cell adhesion molecule the intact function of which is crucial for the establishment and maintenance of epithelial tissue polarity and structural integrity. Mutations in CDH1 occur in diffuse type gastric cancer, lobular breast cancer, and endometrial cancer. In human cancers, partial or complete loss of E-cadherin expression correlates with malignancy. During apoptosis or with calcium influx, E-Cad is cleaved by the metalloproteinase to produce fragments of about 38 kDa (E-CAD/CTF1), 33 kDa (E-CAD/CTF2) and 29 kDa (E-CAD/CTF3), respectively. E-Cad has been identified as a potent invasive suppressor, as downregulation of E-cadherin expression is involved in dysfunction of the cell-cell adhesion system, and often correlates with strong invasive potential and poor prognosis of human carcinomas. |
| Reference |
