Mouse E-Selectin / CD62e / SELE Protein
CD62E,E-selectin,Elam
- 100ug (NPP3472) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50736-MCCH |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD62E,E-selectin,Elam |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse SELE comprises 543 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 59.3 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 70 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Trp 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 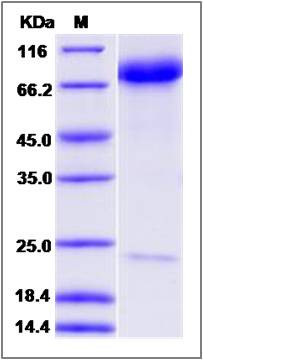 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse SELE (NP_035475.1)(Met1-Pro564) was expressed with six amino acids (LEVLFQ) at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of U937 cells. When 5 x 10E4 cells/well are added to SELE-coated plates (2 μg/mL and 100 μL/well), approximately >70% cells will adhere specifically after 60 minutes at 37℃. |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Embryogenesis |Germ Layer Formation |Mesoderm Marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | E-selectin, also known as endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) and CD62E, is an inducible adhesion molecule that is expressed on the surfaces of stimulated vascular endothelial cells and is sometimes involved in cancer cell metastasis. E-selectin exhibits a complex mosaic structure consisting of a large extracellular region comprised of a lectin domain, an EGF-like domain, and a short consensus repeat (SCR) domain, followed by a transmembrane region and a relatively short (32 aa) cytoplasmic tail. As a member of the LEC-CAM or selectin family, E-selectin recognises and binds to sialylated carbohydrates including members of the Lewis X and Lewis A families found on monocytes, granulocytes, and T-lymphocytes. E-selectin supports rolling and stable arrest of leukocytes on activated vascular endothelium, and furthermore, it was indicated that it can also transduce an activating stimulus via the MAPK cascade into the endothelial cell during leukocyte adhesion. E-selectin regulates adhesive interactions between certain blood cells and endothelium. The soluble form of E selectin (sE-selectin) is a marker of endothelial activation, and has a potential role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease as raised levels have been found in hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidemia, although its association in established atherosclerosis disease and its value as a prognostic factor is more controversial. soluble E-selectin is inversely associated with the muscular component of the left ventricle, thereby suggesting that the lack of such a reparative factor may be associated with cardiac remodeling in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients. In addition, this adhesion molecule appears to be involved in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. |
| Reference |
