Mouse EPOR Protein (His Tag)
Epor
- 100ug (NPP2721) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50031-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Epor |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse EPOR comprises 236 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 26.2 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent mplecular mass of rmEPOR is approximately 30-35 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ala 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 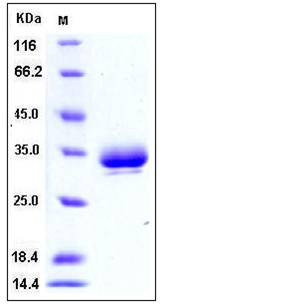 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse EPOR (NP_034279.3) (Met 1-Pro 249) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to inhibit EPO-dependent proliferation of TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.1-0.5 μg/mL in the presence of 16 ng/mL Recombinant mouse EPO. 2. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 3. Immobilized mouse EPOR-His at 10μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind biotinylated mouse EPO-His (P51099-M08H). The EC50 of biotinylated mouse EPO-His (P51099-M08H) is 34.5-80.6ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Transcription Factors and Regulators |HIF Transcription Factors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Erythropoietin (EPO) is the major glycoprotein hormone regulator of mammalian erythropoiesis, and is produced by kidney and liver in an oxygen-dependent manner. The biological effects of EPO are mediated by the specific erythropoietin receptor (EPOR/EPO Receptor) on bone marrow erythroblasts, which transmits signals important for both proliferation and differentiation along the erythroid lineage. EPOR protein is a type â… single-transmembrane cytokine receptor, and belongs to the homodimerizing subclass which functions as ligand-induced or ligand-stabilized homodimers. EPOR signaling prevents neuronal death and ischemic injury. Recent studies have shown that EPO and EPOR protein may be involved in carcinogenesis, angiogenesis, and invasion. |
| Reference |
