Mouse Endoglin / CD105 / ENG Protein (His Tag)
AI528660,AI662476,CD105,Endo,S-endoglin
- 100ug (NPP3296) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50407-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AI528660,AI662476,CD105,Endo,S-endoglin |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse CD105 consists of 565 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 61.2 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 65-70 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Arg 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 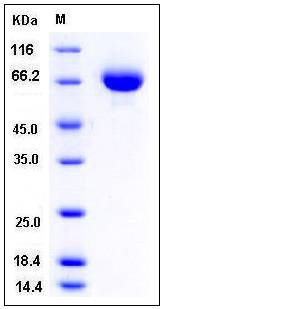 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse CD105 (NP_031958.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Gly 580) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to bind Human ENG-Fc (P10149-H02H) in functional Elisa. 2. Measured by its ability to latent TGFB1-His (P10804-H08H) in functional Elisa. 3. Measured by its ability to mouse ENG-His (P50407-M08H) in functional Elisa. 4. Measured by its ability to inhibit BMP9-induced alkaline phosphatase production by MC3T3E1 mouse chondrogenic cells. David, L. et al. (2007) Blood 109:1953. The ED50 for this effect is typically 5-15 ng/mL in the presence of 2 ng/mL of recombiant human BMP9. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cytokines & Growth Factors |Cytokine & Receptor |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Superfamily |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Family |TGF-beta Family Receptor | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Endoglin, also known as CD105, is a type I homodimeric transmembrane glycoprotein with a large, disulfide-linked, extracellular region and a short, constitutively phosphorylated cytoplasmic tail. Endoglin contains an RGD tripeptide which is a key recognition structure in cellular adhesion,,suggesting a critical role for endoglin in the binding of endothelial cells to integrins and/or other RGD receptors. Endoglin is highly expressed on vascular endothelial cells, chondrocytes, and syncytiotrophoblasts of term placenta. It is also found on activated monocytes, mesenchymal stem cells and leukemic cells of lymphoid and myeloid lineages. As an accessory receptor for the TGF-β superfamily ligands, endoglin binds TGF-β1 and TGF-β3 with high affinity not by itself but by associating with TGF-β type I I receptor (TβRII) and activates the downstream signal pathways. In addition, in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, ALK-1 is also a receptor kinase for endoglin threonine phosphorylation, and mutations in either of the two genes result in the autosomal-dominant vascular dysplasia, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT). Endoglin has been regarded as a powerful biomarker of neovascularization, and is associated with several solid tumor types. |
| Reference |
