Mouse EphA1 / EPH receptor A1 Protein (His Tag)
5730453L17Rik,AL033318,Eph,Esk
- 100ug (NPP3300) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50827-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 5730453L17Rik,AL033318,Eph,Esk |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse EPHA1 comprises 535 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 58.6 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rmEPHA1 is approximately 68 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Arg 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 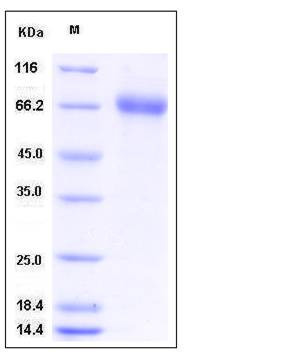 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse EPHA1 (Q60750) (Met 1-Glu 548) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized mouse EPHA1-His at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind mouse EFNA1-Fc (P50593-M02H), The EC50 of mouse EFNA1-Fc (P50593-M02H) is 21.3-49.8 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Protein Phosphorylation |Tyrosine Kinase |Receptor Tyrosine Kinases |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | EPHA1 or EPH receptor A1 belongs to the ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein-tyrosine kinase family. Receptors in the EPH subfamily typically have a single kinase domain and an extracellular region containing a Cys-rich domain and 2 fibronectin type III repeats. An important role of Eph receptors and their ligands ephrins is to mediate cell-contact-dependent repulsion. Eph receptors and ephrins also act at boundaries to channel neuronal growth cones along specific pathways, restrict the migration of neural crest cells, and via bidirectional signaling prevent intermingling between hindbrain segments. Eph receptors and ephrins can also trigger an adhesive response of endothelial cells and are required for the remodeling of blood vessels. Eph receptors and ephrins have emerged as key regulators of the repulsion and adhesion of cells that underlie the establishment, maintainence, and remodeling of patterns of cellular organization. The ephrins and Eph receptors are implicated as positional labels that may guide the development of neural topographic maps. |
| Reference |
