Mouse EphA2 Protein (His Tag)
AW545284,Eck,Myk2,Sek-2,Sek2
- 100ug (NPP3301) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50586-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AW545284,Eck,Myk2,Sek-2,Sek2 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse EPHA2 consists of 523 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 58 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rmEPHA2 is approximately 65 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 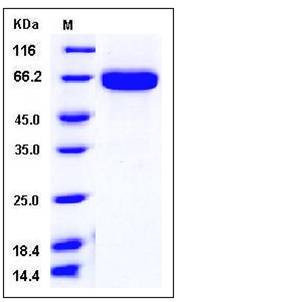 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse EPHA2 (NP_034269.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Asn 535) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 1. Immobilized mouse EphA2 at 2μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind mouse EphrinA1 with a linear range of 0.16-20 ng/ml. 2. Immobilized mouse EphA2 at 2 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human EphrinA1 with a linear range of 0.8-20 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Akt Pathway |Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) in the Akt Pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Eph receptor A2 (Ephrin type-A receptor 2 or EphA2) is a member of the ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein-tyrosine kinase family. The Eph receptors' corresponding family of ligands are the ephrins anchored to cell surfaces. The ephrins and Eph receptors are implicated as positional labels that may guide the development of neural topographic maps. They have also been found implicated in embryonic patterning, neuronal targeting, vascular development and adult neovascularization. The large family of ligands and receptors may make a major contribution to the accurate spatial patterning of connections and cell position in the nervous system. Furthermore, elevated expression of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands is associated with tumors and associated tumor vasculature, suggesting the Eph receptors and ephrin ligands also play critical roles in tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth. Unlike most Eph kinases, which are primarily expressed during development, EphA2 is primarily found in adult human epithelial cells. The cellular functions of EphA2 may be regulating cell growth, survival, migration, and angiogenesis.Unlike other receptor tyrosine kinases, ligand binding is not necessary for EphA2. Rather, the ligand appears to regulate EphA2 subcellular localization and its interactions with downstream adapter and signaling proteins. Eph receptor A2(EphA2) has been demonstrated to critically regulate tumor cell growth, migration and invasiveness. Eph receptor A2(EphA2) is frequently overexpressed and functionally altered in aggressive tumor cells, and that these changes promote metastatic character. |
| Reference |
