Mouse Fetuin-B / FETUB Protein (His Tag)
2310011O17Rik,AI255764,D17980,Gugu
- 100ug (NPP2724) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50572-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 2310011O17Rik,AI255764,D17980,Gugu |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse FETUB consists of 381 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 42.3 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rmFETUB is approximately 55-60 kDa due to high glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Arg 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 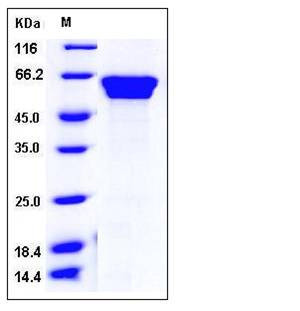 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse FETUB (Q9QXC1-1) (Met 1-Pro 388) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Blood |Serum Protein |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Fetuin-B, also known as Fetuin-like protein IRL685 and FETUB, is a secreted protein which belongs to the fetuin family. Fetuin-B / FETUB contains two cystatin domains. Fetuin-B is a member of the fetuin family, part of the cystatin superfamily of cysteine protease inhibitors. Fetuins have been implicated in several diverse functions, including osteogenesis and bone resorption. Fetuin-A has been identified as a major protein during fetal life and is also involved in important functions such as protease inhibitory activities and development-associated regulation of calcium metabolism and osteogenesis. Fetuin-A is a key partner in the recovery phase of an acute inflammatory response. Fetuin-B / FETUB is found at least in human and rodents. It is unambiguously a paralogue of Fetuin-A. Fetuin-A and Fetuin-B exhibit significant differences at the amino acid sequence level, notably including variations with respect to the archetypal fetuin-specific signature. |
| Reference |
