Mouse GPNMB / Osteoactivin Protein (His Tag)
DC-HIL,Dchil,ipd
- 100ug (NPP3344) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50475-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | DC-HIL,Dchil,ipd |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse GPNMB comprises 490 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 54.9 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 96 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Lys 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 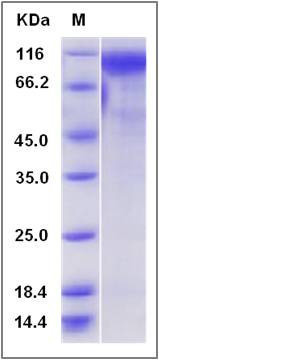 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse GPNMB (Q99P91) (Met1-Asn502) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Organogenesis |Skeletal development |Other Bone Remodeling Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | GPNMB belongs to the PMEL / NMB family, also known as Osteoactivin and Hematopoietic growth factor-inducible neurokinin 1 ( HGFIN ), is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is expressed in numerous cells, including osteoclasts, macrophages, dendritic cells, and tumor cells. It is suggested to influence osteoblast maturation, cell adhesion and migration. GPNMB protein acts as a downstream mediator of BMP-2 effects on osteoblast differentiation and function. GPNMB participates in bone mineralization, and functions as a negative regulator of inflammation in macrophages. Osteoactivin is expressed at high levels in normal and inflammatory liver macrophages suggesting a significant role in acute liver injury. The early-phase upregulation of Osteoactivin expression in the tubular epithelium in response to renal injury might play a role in triggering renal interstitial fibrosis via activation of matrix metalloproteinase expression and collagen remodeling in rats. Osteoactivin as a protein that is expressed in aggressive human breast cancers and is capable of promoting breast cancer metastasis to bone. |
| Reference |
