Mouse HSPD1 / HSP60 Protein (His Tag)
60kDa,Hsp60
- 100ug (NPP3352) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50596-M07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | 60kDa,Hsp60 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse HSP60 consisting of 583 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 62.3 kDa. rmHSP60 migrates as an approximately 58 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 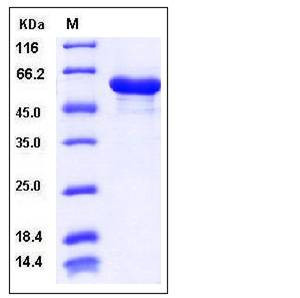 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse HSP60 (NP_034607.3) (Leu 2-Phe 573) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Apoptosis |Intracellular | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | HSPD1, also known as HSP60, is a member of the chaperonin family. HSPD1 may function as a signaling molecule in the innate immune system. This protein is essential for the folding and assembly of newly imported proteins in the mitochondria. It may also prevent misfolding and promote the refolding and proper assembly of unfolded polypeptides generated under stress conditions in the mitochondrial matrix. HSPD1 gene is adjacent to a related family member and the region between the 2 genes functions as a bidirectional promoter. Several pseudogenes have been associated with this gene. Mutations associated with this gene cause autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia 13.Defects in HSPD1 are a cause of spastic paraplegia autosomal dominant type 13 (SPG13). Spastic paraplegia is a degenerative spinal cord disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Defects in HSPD1 are the cause of leukodystrophy hypomyelinating type 4 (HLD4); also called mitochondrial HSP60 chaperonopathy or MitCHAP-60 disease. HLD4 is a severe autosomal recessive hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. HSPD1 is cinically characterized by infantile-onset rotary nystagmus, progressive spastic paraplegia, neurologic regression, motor impairment, profound mental retardation. Death usually occurrs within the first two decades of life. |
| Reference |
