Mouse IL1R1 / CD121a Protein (Fc Tag)
CD121a,CD121b,IL-1R1,IL-iR,Il1r-1
- 100ug (NPP3371) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50807-M02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD121a,CD121b,IL-1R1,IL-iR,Il1r-1 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse IL1R1/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 560 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 64.3 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 70 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Leu 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 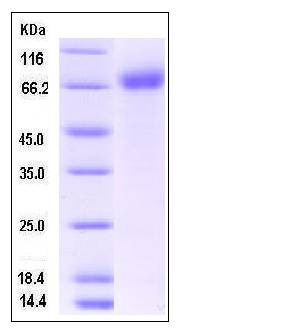 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse IL1R1 (P13504) extracellular domain (Met 1-Lys 338) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized recombinant human IL1b (P10139-HNAE) at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can mouse IL1R1-Fc (P50807-M02H) with a linear range of 62.5-1000 ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Inflammatory Disorders Therapeutic Targets |Rheumatoid arthritis Therapeutic Targets |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interleukin 1 receptor, type I (IL-1R1) also known as CD121a (Cluster of Differentiation 121a), is an interleukin receptor. IL-1R1/CD121a is a cytokine receptor that belongs to the interleukin 1 receptor family. This protein is a receptor for interleukin alpha (IL1A), interleukin beta (IL1B), and interleukin 1 receptor, type I (IL1R1/IL1RA). IL-1R1/CD121a is an important mediator involved in many cytokine induced immune and inflammatory responses. This protein has been characterized by pharmacological and molecular techniques in the mouse brain. The spindle-shaped astrocytes enclose the wound, separating the healthy from damaged neural tissue. The shape change and subsequent repair processes are IL-1β activity-dependent, acting through the IL-1 type 1 receptor (IL-1R1), as co-application of the IL-1type 1 receptor antagonist protein (IL-1ra) blocks IL-1β induced effects. In the spleen, a slight increase in IL-1R AcP and IL-1R1 was observed during the first hours following LPS stimulation. In conclusion, IL-1R AcP mRNA is expressed in the brain and in other tissues where IL-1R1/CD121a transcripts are found. However, the regulation of its expression is distinct from IL-1R1/CD121a. The high level of expression and the lack of regulation of IL-1R AcP transcripts in the brain under inflammatory conditions suggest that the protein might be constitutively expressed in excess. |
| Reference |
