Mouse IL2RG / CD132 Protein (His Tag)
CD132,gamma(c),gc,[g]c
- 100ug (NPP3204) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50087-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD132,gamma(c),gc,[g]c |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse IL2RG consists of 252 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 30 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rm IL2RG is approximately 50-55 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Trp 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 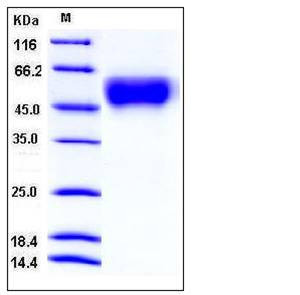 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Ala 263) of mouse IL2RG (NP_038591.1) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cytokines & Growth Factors |Cytokine & Receptor |Interleukin & Receptor |Other Interleukin & Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The common gamma chain (γc) (or CD132), also known as interleukin-2 receptor subunit gamma or IL2RG, is a member of the type I cytokine receptor family expressed on most lymphocyte (white blood cell) populations, and its gene is found on the X-chromosome of mammals. The common gamma chain (γc) (or IL2RG), is a cytokine receptor sub-unit that is common to the receptor complexes for at least six different interleukin receptors: IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15 and interleukin-21 receptor. It is a component of multiple cytokine receptors that are essential for lymphocyte development and function. X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (XSCID) is a rare and potentially fatal disease caused by mutations of IL2RG, the gene encoding IL2RG. IL2RG was demonstrated to be a component of the IL-4 receptor on the basis of chemical cross-linking data, the ability of IL2RG to augment IL-4 binding affinity. The observation that IL-2R gamma is a functional component of the IL-4 receptor, together with the finding that IL-2R gamma associates with the IL-7 receptor, begins to elucidate why deficiency of this common gamma chain (gamma c) has a profound effect on lymphoid function and development, as seen in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. |
| Reference |
